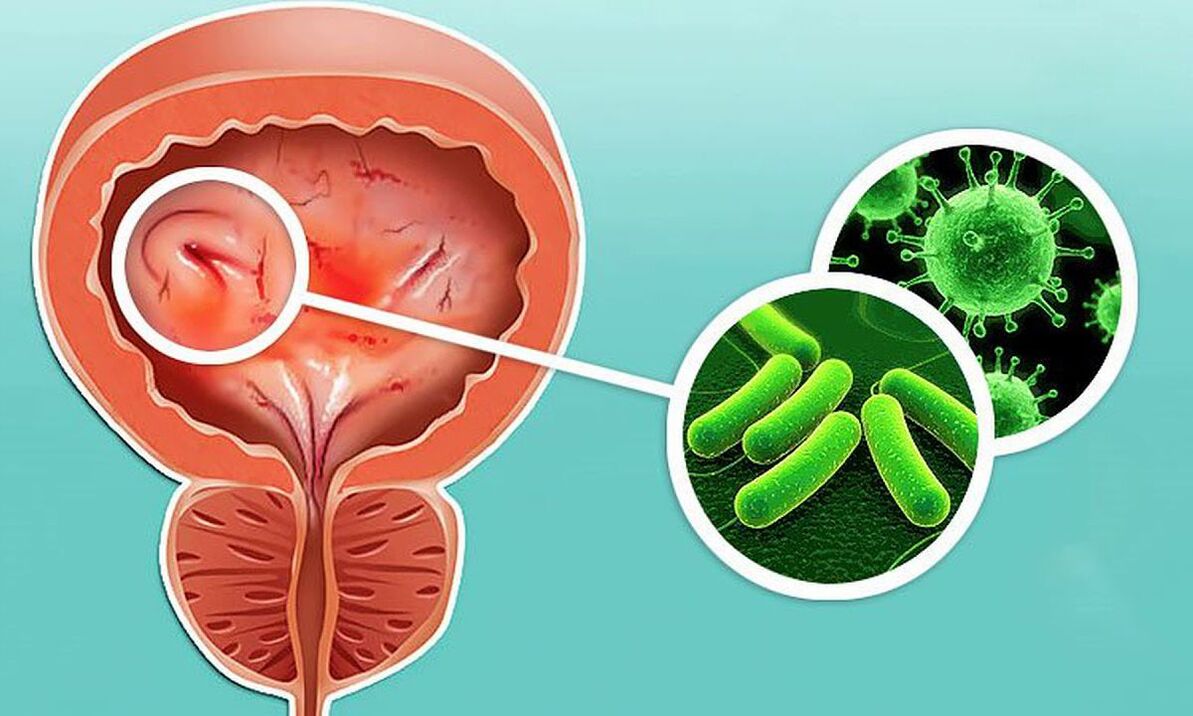
Cystitis (cyctitis) is a common disease of the urinary system, which is associated with the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the bladder. It is noteworthy that every fourth woman has faced the symptoms of cystitis at least once in her life, while every tenth woman suffers from the chronic form of this disease. It is also worth comparing the incidence of women and men: only 0. 5% of men suffer from cystitis, which is mainly due to the difference in the structure of the urethra and the difficulty of the infection entering.
Causes of the disease
In women, cystitis usually occurs due to an aggressive opportunistic pathogen entering the urethra, as well as ascending sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, ureaplasma (Ureaplasma), fungal infections of the genus Candida, etc. The short and wide urinary system is often susceptible to such infections. In women, the occurrence of cystitis can also occur due to the movement of pathogens through the bloodstream. This path of development of the disease is called hematogenous.
Another possibility of infection is the entry of bacteria into the bladder with pathologies of the kidneys and ureters. Usually, such a development of events is observed in pyelonephritis.

It should be noted a less common, but still occurring version of the development of the disease, which is caused by abnormalities in the development of the urinary system. In addition, a decrease in the contractility of the bladder muscles can lead to cystitis.
Signs of infection can appear especially actively in the presence of predisposing factors. These include:
- Sedentary work. Sitting for more than three hours in a row stagnates urine, which leads to a possible infection of the bladder. Therefore, if your job involves long periods of sitting in one place, you should get up every hour and do a little warm-up every three hours.
- Constipation.
- Presence of sand and stones in the bladder.
- Tight underwear that can interfere with the normal blood circulation of the pelvic organs.
- Frequent hypothermia of the body.
- Lower back injury, spinal cord injury.
- Early onset of sexual activity.
- Metabolic disorders, hormonal changes in the body (e. g. menopause or pregnancy). During hormonal waves, the body's immune system can fail. Attention: when carrying a child, the expectant mother is particularly at risk of developing infections and cystitis. Therefore, you should carefully monitor your own health during pregnancy and consult a doctor at the first signs of illness.
- Diabetes mellitus (Diabetes mellitus).
- Therapy with immunosuppressive drugs.
- Oncological diseases.
- Unbalanced and irregular diet: spicy and fried foods, alcohol abuse.
- Improper hygiene practices (especially improper washing from the anus to the vagina).
- The chance of bladder infection is high with inadequate personal hygiene (long-term wearing of the same pad or tampon during menstruation, premature change of underwear, continuous use of daily pads).
- Stress, chronic lack of sleep, which seriously affects the state of immunity.
- A general decrease in immunity caused by a chronic inflammatory focus in the body (stomatitis (stomatitis), tooth decay (caries), rhinitis (runny nose), tonsillitis (tonsillitis). sterility of the urethra
A form of cystitis, such as interstitial cystitis, which is the result of serious disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and is a serious chronic disease, is worth highlighting.
Symptoms and signs

The symptoms of cystitis are very characteristic and allow the correct diagnosis to be made immediately. First of all, these are frequent urination (the patient visits the toilet several times an hour) and the manifestation of pain at the end of the bladder emptying process. In addition, the most prominent symptoms are:
- a feeling of fullness in the bladder even after urination;
- a mixture of blood or pus in the urine;
- urine with cystitis in women has a more pungent smell;
- cloudy urine and the presence of flakes in it;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- when the infection spreads, including the upper part of the urinary system, there may be pain in the kidneys and lower back;
- quite rare, but still having difficulty holding back urine
If you notice these symptoms in yourself, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and further treatment, since the advanced form of the disease is associated with many complications.
The symptoms of cystitis cause not only physical but also psychological discomfort to a woman and leave a mark on her personal and social life. Therefore, it is necessary to react as soon as possible to the appearance of the first signs of the disease and start therapy.
If the inflammation caused by the infection spreads to the muscle layer of the bladder, the appearance of the interstitial form of cystitis, which we have already discussed, is possible. In this case, the urine is directed into the walls of the organ, as well as its return into the ureters.

If not treated, and if the infection spreads vertically, kidney disease, pyelonephritis may develop.
Types of cystitis
It is necessary to distinguish between types of the disease, which differ in the way of occurrence, course, morphological changes and the nature of spread.
All types of cystitis are divided into acute and chronic according to the nature of the course. We consider both options for the course of the disease.
Acute cystitis
Against the background of the symptoms described above, acute cystitis causes low-grade fever and general malaise. The vessels of the bladder expand, which leads to swelling of the walls of the organ. In this case, punctate bleedings and hyperemia (Hyperemia) can be observed. In the acute phase of the disease, the mucous membrane and submucous membrane of the bladder usually suffer, their epithelium is sometimes rejected, and a mixture of blood may appear in the urine. The color of urine in the hemorrhagic form of the disease can vary from light pink to cloudy brown.
Chronic cystitis
When the disease enters the chronic phase, the inflammation expands and spreads from the mucosa and submucosa to the muscle layer of the bladder. In this case, the color of the mucous membrane acquires a whitish or grayish tint. If the disease is not treated for a long time, sclerotic processes appear in the organ, due to which its volume may decrease.
In a chronic form, all the previously mentioned signs can be "blurred" and faintly expressed, which complicates the diagnosis. In case of suspicion of chronic cystitis, the focus should be on the anamnesis, macro and microscopic examination of urine, cystoscopy, and bacteriological examination. A parallel gynecological examination is particularly important in the detection of chronic cystitis, as infections of the genital organs often cause the appearance of chronic forms of cystitis.
Acute and chronic cystitis: which doctor should I consult?
Standard tests for the diagnosis of cystitis in older women, mature women and girls are general urinalysis, urine culture to detect abnormal flora (bacteriuria), Nechiporenko analysis. As an additional measure, modern clinics often offer ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys, cystoscopy and testing for STIs. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe a urine sample for analysis, not by the usual method, but by using a catheter. This may be necessary to prevent vaginal secretions from entering the urine.
Acute cystitis is treated with antibacterial drugs. Given that such drugs are excreted through the kidneys, it is very easy to achieve the desired concentration of the antibiotic in the bladder, so that the effect of the treatment appears as quickly as possible. In doing so, two important factors must be taken into account:
After receiving the results of the urine culture, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics, which determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to the selected drug.
Even after the condition has subsided, the prescribed course of antibiotics must be taken to avoid a relapse and the transition of the disease into a chronic form.

The following should be used as additional measures for the treatment of cystitis:
- medicines to relieve bladder spasms, general anti-inflammatory drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- ozone therapy;
- acupuncture.
To treat the chronic form of cystitis, local administration of drugs that prevent the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms can also be used. Tea tree essential oil gel can be used as an aid. The gel is recommended for eliminating vaginal discomfort, normalizing the microflora and restoring the mucous membrane of the vagina after infectious and inflammatory diseases, as well as in the period following antibiotic treatment.
Acute cystitis
It is worth noting that the treatment of acute cystitis is always bed rest. Treating the inflammatory process of the bladder "on the run" without issuing sick leave, especially in the cold season, means the risk of the disease transitioning into a chronic form. The disease is always accompanied by severe stress for the body, which requires rest and relaxation. At the same time, ignoring the disease anddelaying a doctor's visit can result in pyelonephritis, the treatment of which requires constant medical supervision.
Diet
In order to alleviate the inflammation as soon as possible, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids: the minimum amount of fluid should be 1. 5 liters per day.
Cystitis nutrition has many restrictions. The exclusion of spicy and spicy contributes to healing and avoids the recurrence of the situation. During the treatment period, alcohol should be completely excluded. This applies to all alcoholic beverages.
If you experience painful and frequent urination, blood stains, flakes or pus in your urine, do not panic. In fact, according to statistics, female cystitis is a very common occurrence.
The most important thing is not to delay and see a doctor on time.
Usually, this disease is determined when the urine is often painful in small amounts, with blood stains. Such processes are often accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Cystitis becomes a dangerous chronic form or develops nephritis. Most often, cystitis is infectious.
Cystitis is widespread among women and men, but due to the anatomical features of the female body, the fair sex is more likely to suffer from this disease. The female urethra is shorter and wider than the male urethra, making it easier for pathogens to enter the bladder. This explains the frequent cases of cystitis in women. Women of childbearing age are most susceptible to cystitis. There are many cases of recurrence of cystitis, which significantly worsens a woman's health and affects her life.
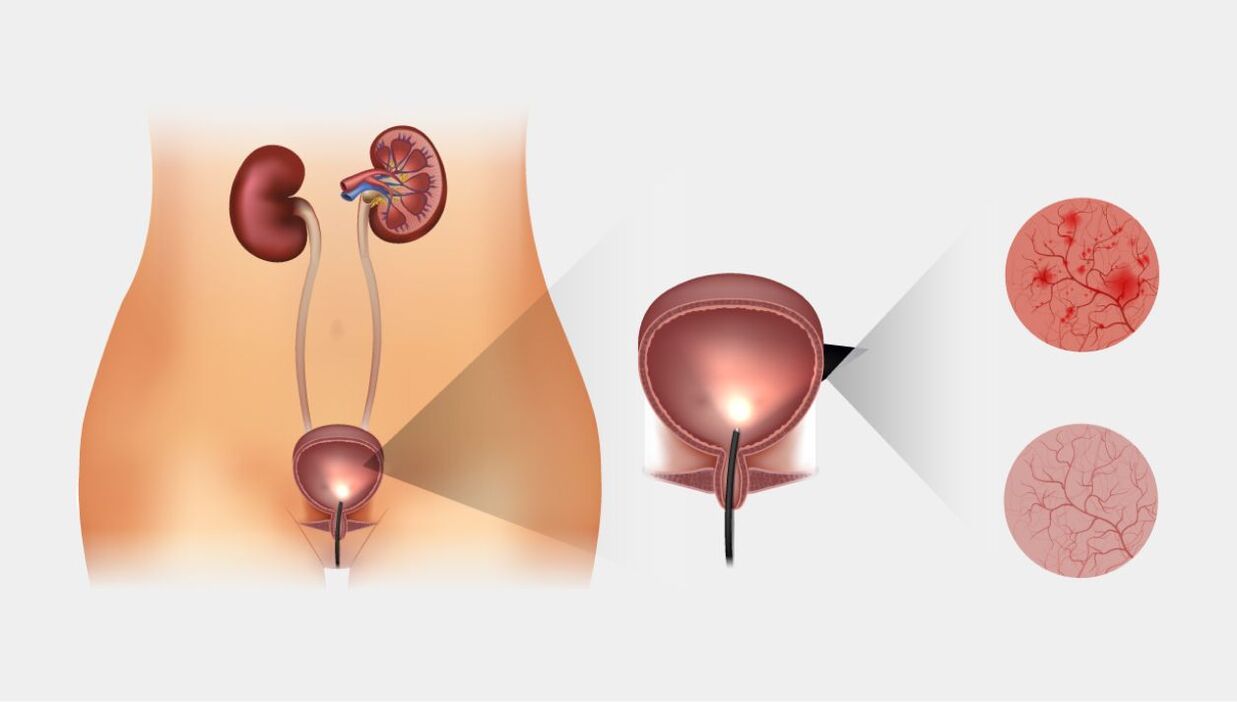
Occurrence of cystitis
The so-called acute cystitis is one of the most common urological diseases. Uncomplicated cystitis is not uncommon, during which the microbes only affect the mucosa, not the submucosal layer.
Based on scientific research, it can be said that 26-36 million people in Hungary suffer from acute cystitis every year.
Girls suffer from cystitis almost three times more often than boys. The disease is occasionally diagnosed in newborns and children under 1 year of age, and is more common in children aged one to three years, but especially in children aged 13 to 15 years. Cystitis usually occurs in patients aged 4-12 years.
Chronic cystitis is one of the most common urological diseases. Based on these tests, chronic cystitis is observed in 11-21% of the population. The significant dispersion of the data is caused by different approaches to the definition of chronic cystitis. The authors of some studies write that the diagnosis of "chronic cystitis" should be considered if the exacerbation occurs twice or more per year.
cystitis in summer
There are very few women who have not felt the symptoms of cystitis when the joy of the wonderful summer days was overshadowed by such an unpleasant disease. In addition, in the summer, especially when a woman travels a long distance from home and finds herself in an unusual environment, there can be many reasons for the appearance of cystitis.
Cystitis most often occurs in the summer season due to the following factors:
- living in a new place during the holiday period, which causes personal hygiene problems;
- hypothermia of the body, which occurs as a result of prolonged bathing in cold water;
- violation of the usual urination schedule, which is associated with moving, flying or staying in a new place;
- drastic climate change that adversely affects human immunity.
In some cases, an additional risk factor for the development of cystitis is an increase in sexual activity against the background of the above conditions, which are unfavorable for the female body.
If your weekend or vacation is spoiled by the occurrence of such an unpleasant disease, you should make an appointment with a urologist as soon as possible. In order to clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound of the bladder must be performed, and a urine test must be submitted. Today, antibacterial drugs effectively act directly on the causative agent of cystitis and can speed up the healing process, as well as prevent the development of acute cystitis into a chronic form.
Modern drugs, unlike the drugs of the last generation, which affected the patient's entire body, only affect the inflamed areas of the bladder, minimally affecting other human organs. The main concentration of the drugs is maximally shown only in the urine and in the mucous membrane of the bladder, which is inflamed. This allows you to minimize the toxic effect on other organs and focus the entire burden on the treatment of cystitis.
Among the drugs used to treat the disease, it is worth mentioning the drug containing fosfomycin. Due to the high selectivity of effects with minimal toxicological burden on the body, it has another useful property - this drug does not cause phototoxicity. This is the name of a side effect that can be caused by many medicines used to treat cystitis. The manifestation of phototoxicity is an increase in sensitivity to sunlight, the occurrence of skin redness or burns under the influence of even low-intensity ultraviolet radiation. Phototoxicity occurs due to the presence of substances in the preparation that have photosensitizing or photoreactive properties. Such substances cause the appearance of a significant amount of free radicals in the skin, which cause the destruction of skin cells, inflammation and even burns.
Unlike other cystitis medications, fosfomycin does not cause phototoxicity, which means it can be used without disrupting your planned beach vacation schedule. The advantage can be called the maximum absence of side effects, and this allows the safe and very effective treatment of cystitis in children and pregnant women.
cystitis during pregnancy
The fair sex is very often interested in the question of how this disease affects pregnancy. Cystitis causes discomfort for all patients, and for a woman in such a situation with a weak immune system, this disease can be a serious test. Pregnant women who face the manifestations of cystitis symptoms have to go through a lot of trouble. Cystitis during pregnancy is undoubtedly dangerous, but timely access to a doctor can prevent unwanted consequences. Self-medication or ignoring the disease can cause very serious complications, such as kidney infection. Bacteria can seriously damage them. The inflamed mucous membrane of the bladder can also have a negative effect on the fetus. There is a chance of giving birth prematurely, with underweight.
Cystitis in children
It is commonly believed that cystitis only affects adults, but this is not the case. Also, there are no age limits for this type of disease. Adults, children and the elderly can also get sick. Both men and women and very young patients suffer from cystitis, but the treatment of cystitis in children has its own peculiarities.
Very often, cystitis in children occurs due to hypothermia. The main causative agent is bacteria, fungal and viral infections are extremely rare.
Causes of cystitis
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the causative agent in 70-95% of patients with acute cystitis, Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus saprophyticus) in 5-20%, and Proteus mirabilis in the remaining patients. the illness. ) and Klebsiella (Klebsiella spp. ).
Cystitis is usually caused by organisms from the opportunistic flora. Studies have confirmed that the causative agents of cystitis are not necessarily bacteria, it is very possible to get cystitis caused by mycoplasma virus, chlamydia, Trichomonas and other fungi.
The high incidence of cystitis among women is due not only to the short length of the urethra, but also to its wide lumen and its physiological location in relation to other organs. The female urethra, unlike the male urethra, is closer to the anus. Due to such anatomical features of the female body, the body is poorly protected against pathogenic microbes entering the urethra, so microbes can easily migrate to the bladder, which can cause cystitis.
Cystitis is less common in men. In men, the most common causes of the disease are inflammation of the urethra, epididymis, seminal vesicles, and prostate. It happens that the penetration of the infection into the area of the urethra occurs due to catheterization. The risk of cystitis doubles after bladder catheterization in men with BPH, where frequent urinary retention is one of the symptoms. The probability of developing cystitis also increases after the introduction of a catheter into a pregnant woman or a woman who has just given birth, this is based on a decrease in the tone of the urinary tract.
Symptoms of cystitis
In adults, cystitis usually causes frequent, painful urination. The nature of the pain is described as a burning sensation. Urine changes, has a strong smell, may become cloudy and contain blood stains. In this case, the state of health may deteriorate and constant pain may be felt in the lumbar region. In the elderly and in children, the symptoms of cystitis are usually not so obvious. They can be characterized by symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain and nausea.
Diagnosis of cystitis
During the diagnosis of the disease, the urologist examines the results of the urinalysis, as well as the results of the ultrasound of the bladder. Bacterial urine cultures are used to determine the etiology of cystitis, and a swab is also taken from the urethra. In most cases, bacteria of opportunistic flora, namely staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, etc. can cause cystitis. Cystitis often occurs due to infection with sexually transmitted pathogens - ureaplasma and mycoplasma. Treatment of cystitis includes the effect of drugs on infectious agents that can provoke the development of the disease.
Treatment of cystitis
A quick cure of cystitis and even complete rehabilitation of the mucous membrane is possible if you do not delay the start of the treatment, but use drugs of adequate effectiveness immediately. The chance of getting rid of cystitis completely increases with timely correct diagnosis and the use of drugs that affect the center of infection. If the treatment is started in the later stages, or a treatment is prescribed that only eliminates the symptoms of cystitis without affecting the causative zone, acute cystitis can turn into chronic.

The main task of the doctor treating cystitis is to destroy the pathogenic microbes that have invaded the bladder area and caused inflammation of the mucous membrane. The drugs required for the course of antibiotic therapy of the disease are determined according to the following parameters: the duration of the disease, the severity of the symptoms. In addition, during the selection of drugs, possible side effects, the way and speed of their elimination, the absorption of the drug, the presence of other diseases, etc. are taken into account.
To date, there are relatively affordable drugs for the treatment of cystitis that selectively affect the causative agent of the disease, a qualified doctor recommends only such treatment. When swallowed, the drug is concentrated inside the bladder, which makes it possible to increase its effectiveness. In addition, the use of modern antibiotics reduces the duration of cystitis treatment, protects as much as possible from side effects, and reduces the risk to the patient's entire body.
Useful tips to prevent cystitis
- try to avoid hypothermia;
- despite the circumstances, carefully observe the rules of hygiene;
- use neutral and gentle products during hygiene procedures;
- during menstruation, change sanitary pads on time;
- visit the toilet on time, do not delay if necessary;
- drink more fluids;
- it is advisable to avoid tight clothing, tk. compression can impair blood circulation in the pelvic area;
- try to normalize bowel function. If you are prone to constipation, you should increase your intake of fresh fruits and vegetables.
In this case, the symptoms and treatment of cystitis will not be a problem for you.